


FeaturesThe relacs software platform offers the following main features: Closed-loop experimentsTraditionally, appropriate stimuli for probing a neuron are generated first. Then some days are spent doing experiments with the new stimuli. Afterwards the preliminary data are analyzed offline. Based on the findings the experimental protocol and the stimuli are modified and new experiments are conducted. 
Closed-loop experiments.
From
Benda et al. 2007.
relacs is designed as an framework for closed-loop experiments that may considerably speed up this traditional approach and in addition offers novel experimental possibilities. In a closed-loop experiment a stimulus is presented (1), the resulting response (2) is analyzed immediately (3), and properties of the next stimulus (4) (mean intensity, standard deviation, spectral content...) are adjusted as needed (see figure). The closed-loop approach is beneficial on many levels, even for traditional experimental paradigms:
Closed-loop experiments, however, also offer new experimental designs:
See our review "From response to stimulus: adaptive sampling in sensory physiology" for more details. Hardware-independent research protocolsCentral to relacs are the "research protocols" (RePros). They control the experiment by analysing and visualizing data and generating stimuli. The relacs-core completely hides all specific hardware details behind the scenes. Therefore research protocols can be implemented independently of the hardware used at a particular experimental setup (data acquisition board, attenuator, temperature sensors, motorized micromanipulators). This allows to use the very same research protocols for all your different experimental setups in your lab, no matter what particular hardware is used. Furthermore, this offers the unique possibility to share research protocols with other labs. Data-analysis libraryrelacs comes with an extensive set of data-analysis functions. The functions are implemented in C++ to allow fast and memory efficient data-analysis as it is required for closed-loop experiments.
New functions are added as required. MetadataFor offline data-analysis, data management, and data sharing the annotation of the raw data with metadata that specify the stimuli, the recorded neuron, the animal, as well as context of the experiment is necessary. Traditionally, such data have been written into lab books. relacs knows already many of the relevant metadata. In particular, these are properties of the generated stimuli and settings of the controlled hardware. Upon completion of a recording, relacs immediately forces the experimenter to provide additional important information through a freely configurable dialog. In addition, for each recording all configuration files, log files, and settings of the research protocols are saved as well. Thus, relacs minimizes manual efforts as much as possible in providing metadata. This is especially important when it comes to data sharing over public databases like G-Node. We developed odML, a file format for hierarchically organized key-value pairs that is independent of any specific database-schema and thus can be used as a general file format for exchanging metadata. Through customized terminologies the metadata can be structured and standardized for ensuring interoperability while at the same time not restricting the content, thus providing immediate flexibility. This way, metadata can be directly submitted to a local as well as public data-bases, like for example the LabLog or the German Neuroinformatics Node, without any manual interference. See our paper "A bottom-up approach to data annotation in neurophysiology" for more details on odML. The NIX project develops generic data models that are tightly linked to meta-data. relacs is using the NIX data model for writing the acquired data and meta-data into a single HD5 file. Dynamic clamp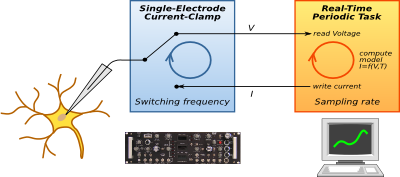
The dynamic clamp. During each sampling cycle a voltage V is read in,
a current I is computed, and this current is injected back into the cell.
The dynamic clamp is a technique that is used in the neurosciences to artificially introduce ionic conductances to a neuron. This is accomplished by a closed-loop system running on a per-sample basis. First, a voltage value is read in. Then, a current is computed depending on that voltage. Finally, this current is injected back into the cell. Dynamic clamp can be easily added to relacs by providing a specific implementation of the AnanlogInput and AnalogOutput device classes. Currently, an implementation based on RTAI real-time Linux and comedi for accessing data acquisition boards is provided (DynClampAnalogInput and DynClampAnalogOutput). Integration of experiment and model simulationsBesides acquiring data from a real experiment, relacs can also run in a simulation mode, where the data are acquired from a model simulation. This is a very important feature, that sets relacs apart from many other data acquisition software:
Models can be implemented as a Model plugin for relacs. Free softwarerelacs is distributed as free software ("free" as in "free speech") under the GNU General Public License (GPL).
|